PCB is an important part of almost all electronic devices. Connect different components and support them to work properly. In high-performance circuits, the selection of PCB materials affects the speed, accuracy and strength of the entire system. Whether working with mobile phones, computers or satellites, it is extremely critical to employ the correct PCB material. In this article, I will discuss how to select PCB materials for high-performance circuits, what materials are available, and what to consider when making a decision.
The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a flat board constructed of non-conductive material (referred to as substrates) and contains copper tracks that conduct electricity between various components. The substrates vary in shape and size according to the product.
The most common PCB types are:
If it is a straightforward circuit, standard materials can be employed. But for high-speed circuits, high-frequency circuits, or those in complex systems like aerospace and telecommunications, special materials have to be chosen to fulfill the more stringent requirements.
Choosing the right PCB material is not just about making sure the board works. It can also be:
Let's look at the materials commonly used in different types of PCBs.
FR-4 is among the widely used PCB material globally. The FR-4 is produced with fiberglass and epoxy resin, outstanding strength and hardness, and inexpensive. The FR4 is simple to process and easily obtainable, so it is used as the norm for most types of electronics. It is also used for general purpose equipment as it can absorb moderate heat and has electrical qualities.

Rogers and Teflon PCB material with high frequency are especially designed for use in circuits required to function at extremely high speed or radio frequency. They help minimize signal loss and have a more stable response as frequency grows. It finds application in modern communication systems where signal quality matters a lot. These materials are more expensive than FR4, and while they are difficult to handle during production, their electrical performance is much better.

Polyimide PCB material is famous for its excellent resistance to heat. It can withstand temperatures much higher than FR4 and continues to perform well even under severe conditions. This makes it appropriate for aerospace, defense, automotive and other applications' electronics. Additionally, polyimide substrates exhibit high flexibility and strength, and this assists where circuits are under vibration and mechanical stress.
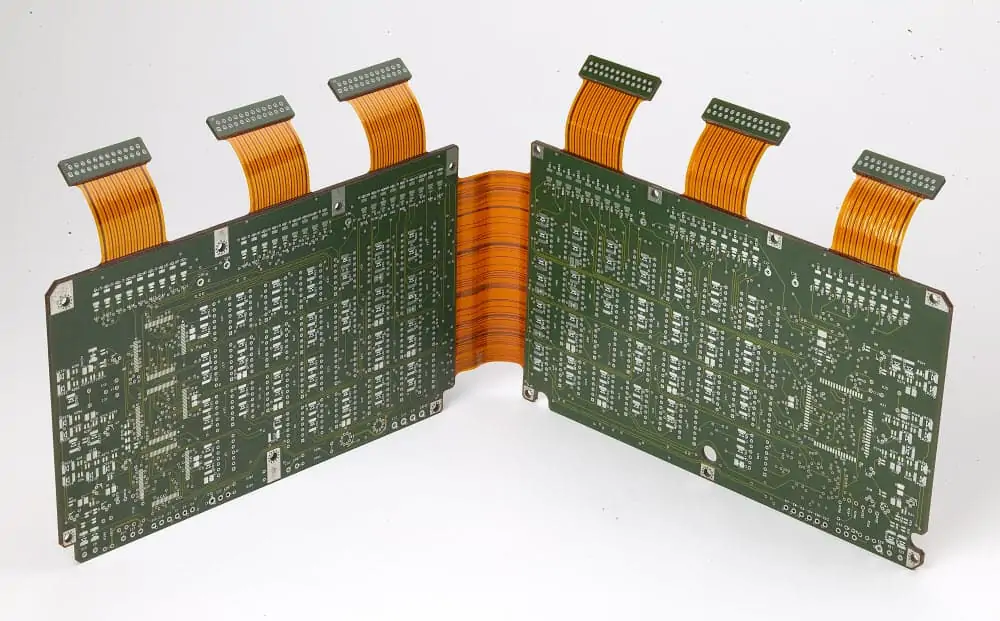
Metal core PCB involves the use of a metal layer (aluminum in most cases). Metal facilitates fast heat removal from the substrate, which is crucial in high-heat generation systems like power supplies and LED lights. The substrates are highly rigid, more resistant to heat than normal PCBs, protecting components and enhancing performance. In the event of heavy and particularly intricate designs, molding becomes challenging.
When choosing a PCB material, it is important to see some technical properties. Let's break them down easily.
Indicates how much energy the material can store. Low values are more suitable for high-speed signal transmission. Materials with a stable dielectric factor perform better in high-speed circuits.
Ideal range: 2.2 ~ 4.5 (suitable for high speed as low)
Indicates how much the signal is lost when moving through the material. The lower the Df, the cleaner and faster the signal.
Ideal range: less than 0.005 for high frequency operation.
Indicates the speed at which the material moves heat. The higher the thermal conductivity, the better to keep the parts at low temperature.
Tg is the temperature at which the material changes from hard to soft. The higher the Tg, the better the performance at high temperatures.
Look for Tg > 170°C for demanding applications.
The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) indicates how much the material expands when heated. The lower the CTE, the less stress on components during heating and cooling.
If you understand the material and its characteristics, here are the steps to choose the right material.
Ask yourself the following questions:
Once you know your needs, look at various materials to see which materials are best suited. For example”
PCB manufacturers give you the right advice based on your experience. In addition, we may teach you materials that are in stock and materials that can be easily worked.
When choosing a PCB material, please note:
| Application Type | PCB Material Used | Reason |
| Mobile Phones | FR-4 / Modified FR-4 | Low cost, decent performance |
| Satellite Systems | Rogers, Teflon, Polyimide | High-frequency, heat resistance |
| LED Lighting | Aluminum Core | Good heat control |
| Automotive ECUs | Polyimide, Ceramic | Handles heat and vibration |
| Wi-Fi Routers | Rogers 4350B | Low signal loss, high speed |
As electronics become smaller and faster, materials need to be improved. Some trends to note
Selecting the right PCB material is very important for building high-performance circuits. Not only does the circuit work, but it also involves good operation, life and final cost. By understanding circuit needs and comparing the properties of materials, you can make smart choices that lead to better products. Always check the dielectric rate, signal loss, heat treatment and cost. Also, if you don't know, consult a manufacturer or an engineer with experience in the type of circuit you are trying to make. Using the right materials, the circuit works faster, keeps it at a lower temperature, and works more reliably.


Please contact us to experience the difference with high quality of HongRong (shenzhen) Electronics Co.,Ltd.